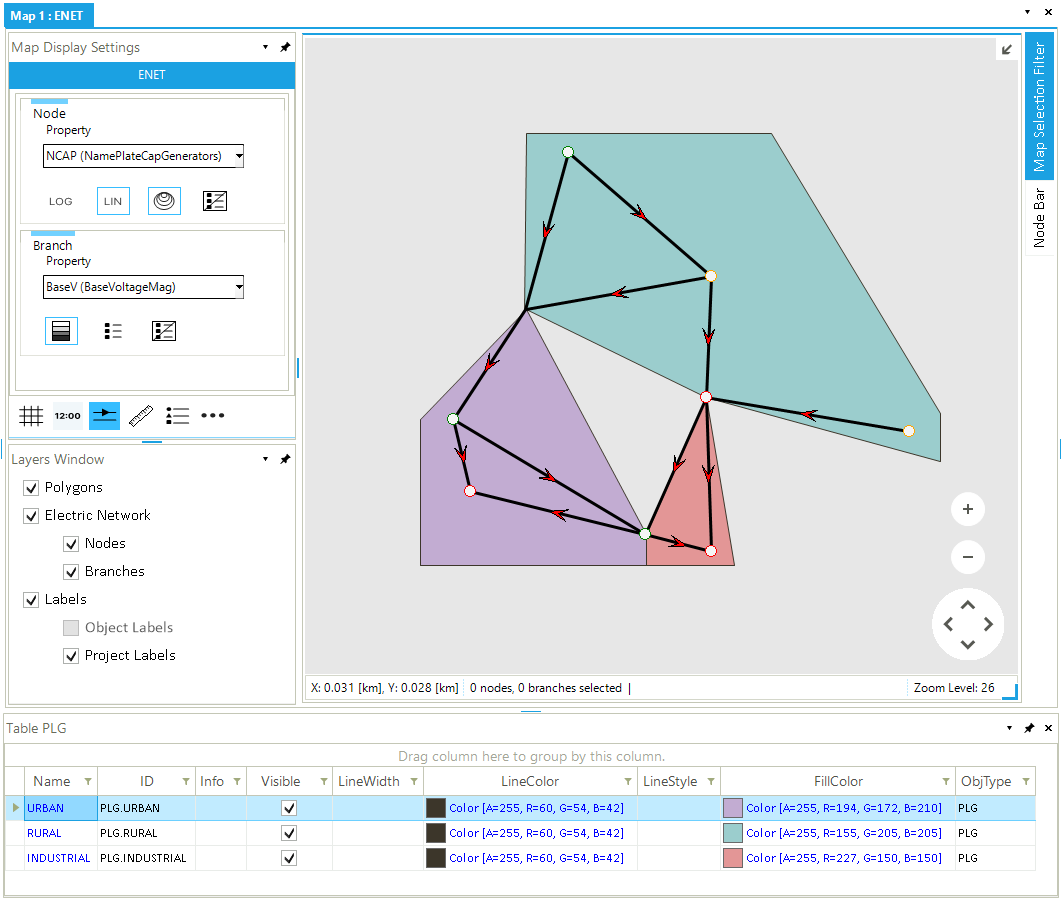
Edit Properties of Polygons
1. Access properties
Properties of a polygon can be accessed and changed in different ways in SAInt. One way is to select the polygon you want to edit in the polygons list of the model explorer (❶ in Figure 1). Then, right-click and select Open Editor. Alternatively, if it is already open, check the property editor after selecting the polygon (❸). A second approach is to use the Polygons Table. An overview of all editable properties is available by clicking the button PLG (❷ in Figure 1) in the table menu of the main window. When multiple polygons are selected, the Multi Edit option is available from the context menu after right-clicking.
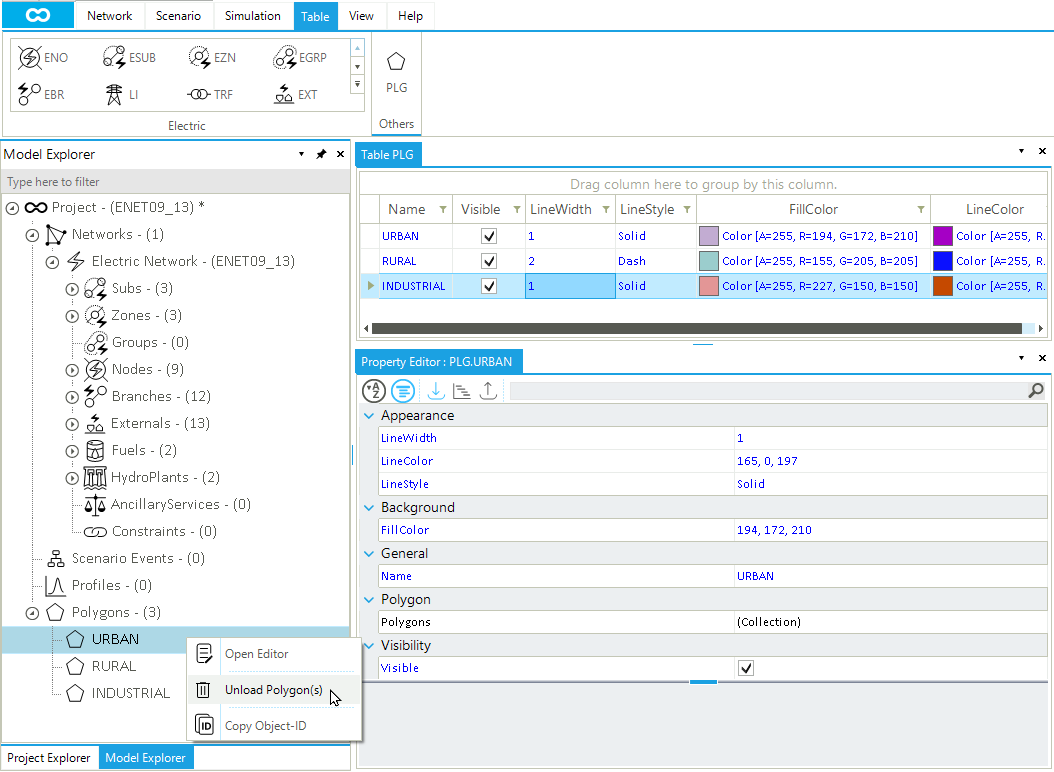
2. The polygon table
The polygon table is the best place to manage and edit all relevant properties (Figure 2). Double-click on any cell to start editing its content. The attributes shown in the table can be easily personalized by hiding existing columns or displaying new columns. Right-click on any cell’s header and select the Hide Column or the Choose Column to change the table. Rows can be sorted or filtered as any other table in SAInt.
The main graphical properties are the fill color and the line color of the polygon boundary. Just double-click and modify the RGB values of the numerical sequence. Also, each polygon has a label, which is a combination of the property Name and the property NatID (i.e., the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code for a country). The color of this label can be modified from the table or can be changed in the property editor along with the font family and the font size.
By accessing the context menu from a row in the polygons table, the user can:
-
open the property editor for the selected polygon.
-
unload the polygon from the list of available polygons and remove it from the map view. This is not a deleting operation.
-
edit the content of the cell, when possible.
-
copy the
IDof the polygon.