Step 4: Build a Steady State Scenario
In the previous steps of this beginner tutorial, you created a simple mashed thermal network with nine pipelines, two supply points, and six demand points. Now, you will complete the model with a scenario to simulate a possible steady state condition. This step will describe how to set up a steady state scenario and add events in SAInt to influence the model’s behavior.
|
If you closed SAInt at the previous step and saved your work, you can restart from where you left off by following these steps:
|
1. Scenario creation
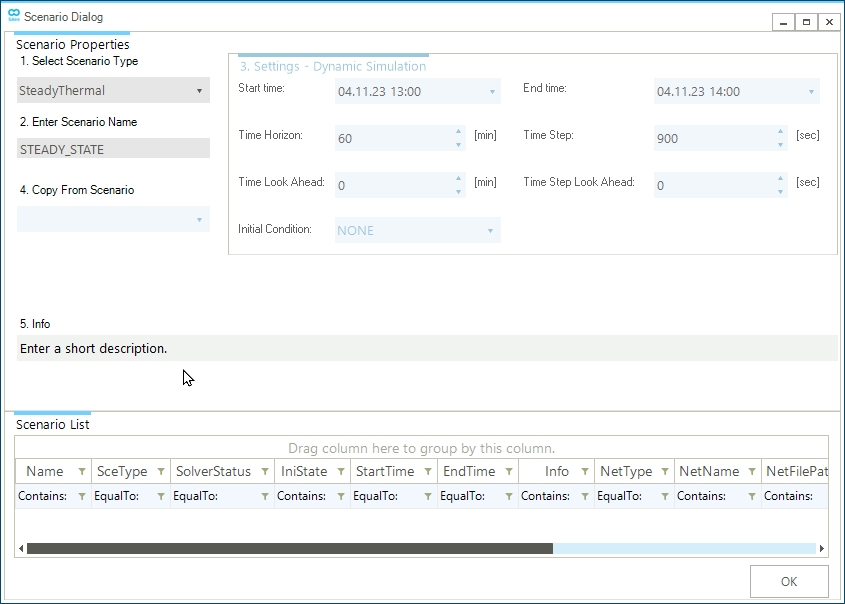
Create a new scenario by going to the scenario tab and selecting . This will open the scenario dialog window, where you will define the parameters and settings of the scenario. The first step is to define the scenario type in the top left corner under 1. Select Scenario Type click on the drop-down menu and select SteadyThermal. Under 2. Enter Scenario Name enter STEADY_STATE as shown in Figure 1. You can enter a short description of your new scenario in 5. Comment. The scenario name will also be used to name the scenario file. In this case, the file will be named STEADY_STATE.tsce. Once completed, click OK at the bottom of the window. A prompt will show up that indicates the scenario was created successfully. Close the window or press OK to continue.
2. Add events for the heat demand points
Once a scenario is available, it is possible to add events. Select the object HDEM.DEMAND3 in the model explorer, and right-click to access from the context menu as in Figure 2. A new window opens where you can define the properties of the event. Set Value to 35 °C. Leave all other properties to their default values.
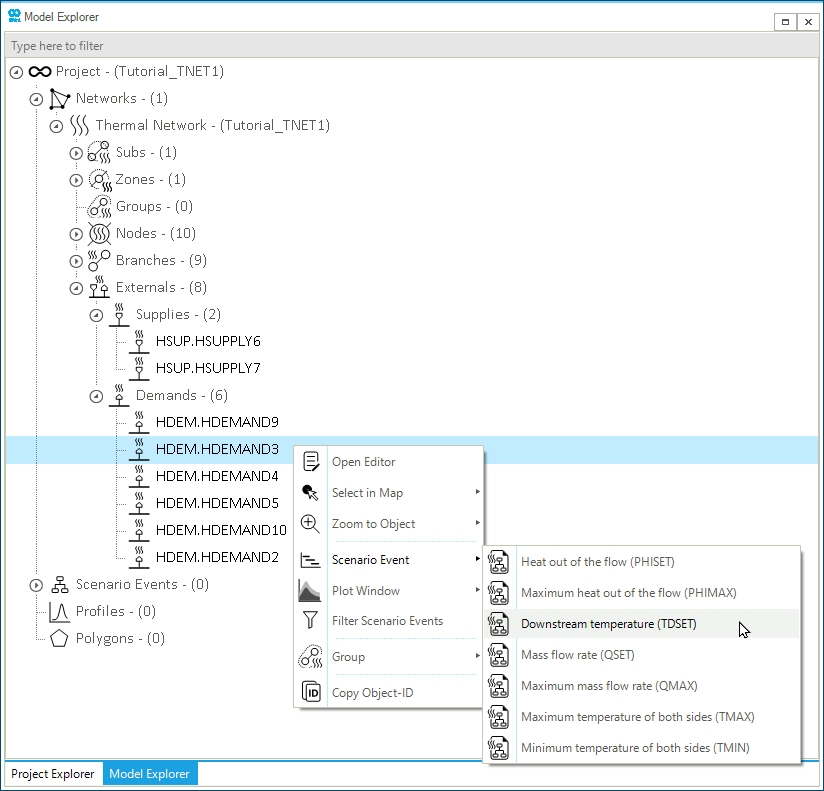
Now select the object HDEM.DEMAND4 in the map window and check the content of the Node Bar. You will see all external and branches connected to the node. In the node bar, select the demand external and right-click to access from the context menu. In the event properties window, set Value to 30 °C. Leave all other properties to their default values.
Use Table 1 to add all necessary events for the demand points.
| Demand Name | Event | Value | Unit of measure |
|---|---|---|---|
DEMAND2 |
|
30 |
°C |
DEMAND3 |
|
35 |
°C |
DEMAND4 |
|
30 |
°C |
DEMAND5 |
|
30 |
°C |
DEMAND9 |
|
30 |
°C |
DEMAND10 |
|
35 |
°C |
DEMAND2 |
|
0.4 |
MW |
DEMAND3 |
|
0.9 |
MW |
DEMAND4 |
|
0.4 |
MW |
DEMAND5 |
|
0.4 |
MW |
DEMAND9 |
|
0.2 |
MW |
DEMAND10 |
|
0.7 |
MW |
3. Add events for the heat supply points
Now, we can add events to model the heat supply side on the tutorial network. Select one of the supply points, and from the context menu, choose . Use the details provided in Table 2 to fill in the value and to complete the scenario with all required events.
Once the thermal events are finished, we need to add a reference hydraulic pressure. Select NODE6 and from the context menu, choose setting a value of 6 bar-g.
| Demand Name | Event | Value | Unit of measure |
|---|---|---|---|
SUPPLY6 |
|
70 |
°C |
SUPPLY7 |
|
90 |
°C |
SUPPLY6 |
|
2.4 |
MW |
SUPPLY7 |
|
2.0 |
MW |
SUPPLY6 |
|
1 |
- |